The hyperlink between local weather change and biodiversity has lengthy been established. Though all through Earth’s historical past the local weather has all the time modified with ecosystems and species coming and going, speedy local weather change impacts ecosystems and species potential to adapt and so biodiversity loss will increase.
From a human perspective, the speedy local weather change and accelerating biodiversity loss dangers human safety (e.g. a serious change within the meals chain upon which we rely, water sources might change, recede or disappear, medicines and different assets we depend on could also be more durable to acquire because the crops and forna they’re derived from might cut back or disappear, and so on.).
The UN’s World Biodiversity Outlook 3, in Could 2010, summarized some issues that local weather change may have on ecosystems:
Local weather change is already having an influence on biodiversity, and is projected to change into a progressively extra vital menace within the coming many years. Lack of Arctic sea ice threatens biodiversity throughout a complete biome and past. The associated stress of ocean acidification, ensuing from increased concentrations of carbon dioxide within the ambiance, can also be already being noticed.
Ecosystems are already exhibiting destructive impacts beneath present ranges of local weather change … which is modest in comparison with future projected modifications…. Along with warming temperatures, extra frequent excessive climate occasions and altering patterns of rainfall and drought could be anticipated to have vital impacts on biodiversity.
Some species might profit from local weather change (together with, from a human perspective, an will increase in illnesses and pests) however the speedy nature of the change suggests that the majority species is not going to discover it as helpful as most will be unable to adapt.
On this web page:
Local weather change impacts on biodiversity within the Arctic
The Arctic, Antarctic and excessive latitudes have had the very best charges of warming, and this pattern is projected to proceed, because the above-mentioned World Biodiversity Outlook 3 notes (p. 56).
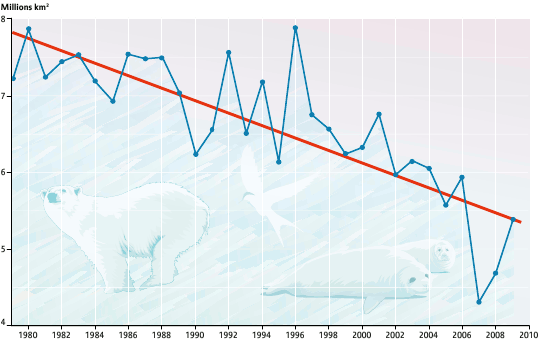
Within the Arctic, it’s not only a discount within the extent of sea ice, however its thickness and age. Much less ice means much less reflective floor which means extra speedy melting. The speedy discount exceeds even scientific forecasts and is mentioned additional on this website’s local weather change introduction.
When it comes to biodiversity, the prospect of ice-free summers within the Arctic Ocean implies the lack of a complete biome
, the World Biodiversity Outlook notes (p. 57).
As well as, Complete species assemblages are tailored to life on high of or beneath ice — from the algae that develop on the underside of multi-year ice, forming as much as 25% of the Arctic Ocean’s major manufacturing, to the invertebrates, birds, fish and marine mammals additional up the meals chain.
The long-lasting polar bear on the high of that meals chain is subsequently not the one species in danger despite the fact that it might get extra media consideration.
Be aware, the ice within the Arctic does thaw and refreeze every year, however it’s that sample which has modified quite a bit in recent times as proven by this graph:
Additionally it is necessary to notice that lack of sea ice has implications on biodiversity past the Arctic, because the World Biodiversity Outlook report additionally summarizes:
- Vivid white ice displays daylight.
- When it’s changed by darker water, the ocean and the air warmth a lot sooner, a suggestions that accelerates ice soften and heating of floor air inland, with resultant lack of tundra.
- Much less sea ice results in modifications in seawater temperature and salinity, resulting in modifications in major productiveness and species composition of plankton and fish, in addition to large-scale modifications in ocean circulation, affecting biodiversity nicely past the Arctic.
(This website’s intro to local weather change and Arctic geopolitics has extra concerning the influence to the Arctic.)
Rising ocean acidification
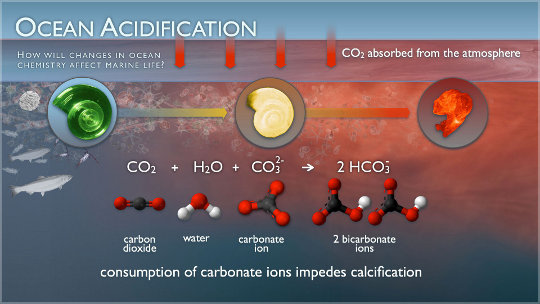
Though it has gained much less mainstream media consideration, the results of accelerating greenhouse emissions — specifically carbon dioxide — on the oceans could be vital.
Scientists have discovered that oceans are capable of soak up a number of the extra CO2 launched by human exercise. This has helped maintain the planet cooler than it in any other case may have been had these gases remained within the ambiance.
Nevertheless, the extra extra CO2 being absorbed can also be ensuing within the acidification of the oceans: When CO2 reacts with water it produces a weak acid referred to as carbonic acid, altering the ocean water chemistry. Because the World Biodiversity Outlook report explains, the water is a few 30% extra acidic than pre-industrial instances, depleting carbonate ions — the constructing blocks for a lot of marine organisms.
As well as, concentrations of carbonate ions at the moment are decrease than at any time over the past 800,000 years. The impacts on ocean organic range and ecosystem functioning will seemingly be extreme, although the exact timing and distribution of those impacts are unsure.
(See p. 58 of the report.)
Though hundreds of thousands of years in the past CO2 ranges had been increased, at the moment’s change is going on quickly, giving many marine organisms too little time to adapt. Some marine creatures are rising thinner shells or skeletons, for instance. A few of these creatures play a vital function within the meals chain, and in ecosystem biodiversity.
Some species might profit from the additional carbon dioxide, and some years in the past scientists and organizations, such because the European Venture on OCean Acidification, shaped to attempt to perceive and assess the impacts additional.
One instance of latest findings is a tiny sand grain-sized plankton chargeable for the sequestration of 25–50% of the carbon the oceans soak up is affected by growing ocean acidification. This tiny plankton performs a serious function in protecting atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations at a lot decrease ranges than they might be in any other case so massive results on them might be fairly severe.
Different associated issues reported by the Inter Press Service embody extra oceanic useless zones (areas the place there’s too little oxygen within the sea to help life) and the decline of necessary coastal crops and forests, akin to mangrove forests that play an necessary function in carbon absorption. That is on high of the already declining ocean biodiversity that has been occurring for a couple of many years, now.
There’s additionally a linkage with local weather change:
Ocean stratification, the place heat water sits firmly on high of chilly, nutrient-rich water, additionally creates useless zones and lowers the general productiveness of the oceans.… Such useless zones had been uncommon 40 years in the past however now quantity a number of hundred. With out pressing motion, local weather change will proceed to heat oceans, growing stratification and producing bigger and extra useless zones with a serious influence on future fisheries, a 2009 examine in Nature Geoscience warned.
It can take a thousand years for the oceans to chill down, so it’s crucial to drag the emergency brake on international warming emissions, the examine concluded.
Coral reefs threatened by local weather change
All over the world, coral reefs have been dying largely resulting from local weather change.


Wholesome coral could be very colourful and wealthy with marine life.
At first of September, 2009, the Australian company taking care of the Nice Barrier Reef launched an outlook report warning the Nice Barrier Reef is in bother.
However it’s not simply the Nice Barrier Reef in danger. All of them are in danger, says Charlie Veron, an Australian marine biologist who’s broadly thought to be the world’s foremost knowledgeable on coral reefs.
The long run is horrific
, he says. There isn’t a hope of reefs surviving to even mid-century in any type that we now acknowledge. If, and when, they go, they may take with them about one-third of the world’s marine biodiversity. Then there’s a domino impact, as reefs fail so will different ecosystems. That is the trail of a mass extinction occasion, when most life, particularly tropical marine life, goes extinct.
Coral reefs present many ecosystem companies to people as nicely, without cost. This website’s web page on coral reefs goes into these points in additional depth.
Lizards threatened by local weather change

What the BBC described as a global-scale examine
revealed within the journal Science discovered that local weather change may wipe out 20% of the world’s lizard species by 2080.
World projection fashions utilized by the scientists prompt that lizards have already crossed a threshold for extinctions brought on by local weather change
.
The concern of lowland species shifting to increased elevations has lengthy been predicted as an impact of local weather change. This has been noticed with lizard populations too, because the chief of the analysis staff informed the BBC: We are literally seeing lowland species shifting upward in elevation, slowly driving upland species extinct, and if the upland species can’t evolve quick sufficient then they’re going to proceed to go extinct.
Why are lizards so delicate to local weather change? The BBC summarizes:
Lizards, the researchers say, are way more inclined to climate-warming extinction than beforehand thought. Many species dwell proper on the fringe of their
thermal limits.Rising temperatures, they defined, depart lizards unable to spend ample time foraging for meals, as they must relaxation and regulate their physique temperature.
Different examples
The above areas of biodiversity affected is certainly not exhaustive. Different areas affected by local weather change embody terrestrial animals, and forests, water sources and associated ecologies, and so forth. For extra data on these areas, see this website’s sections on

